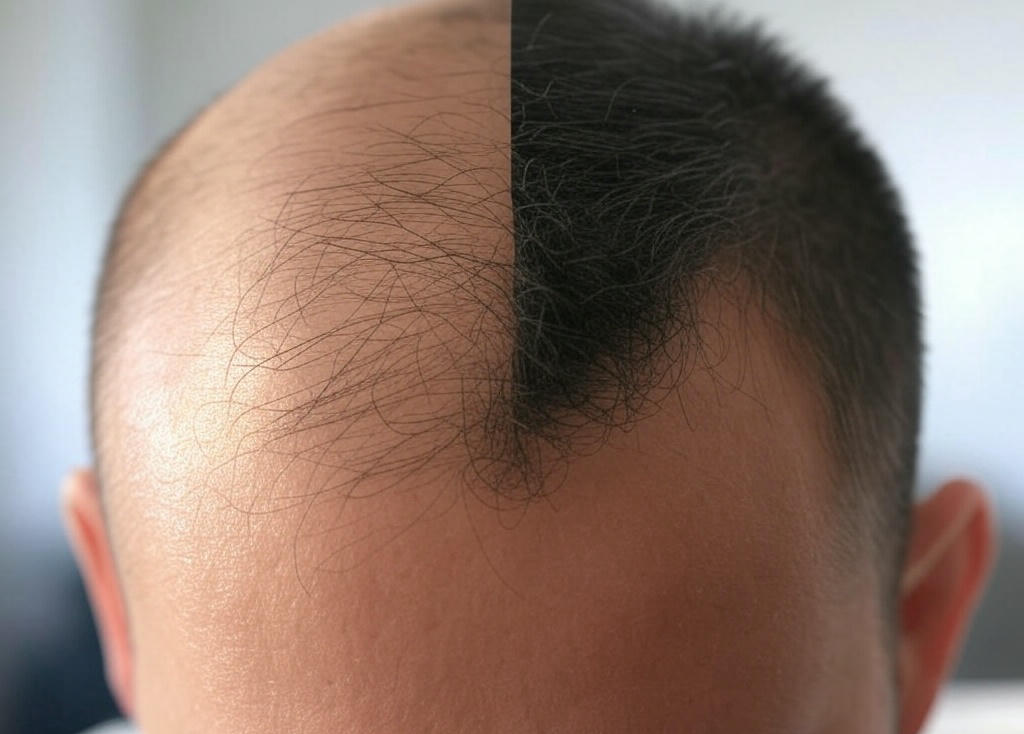
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, whether it happens gradually or suddenly. With over 50 million men and 30 million women affected by various forms of hair loss in the United States alone, it’s a more common condition than you might think. Knowing the specific type of hair loss you’re experiencing is the first step to understanding your options for treatment and prevention.
This guide explores the different types of hair loss, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options to help you take control of your scalp health and hair regrowth.
Hair loss, also called alopecia, occurs when the normal cycle of hair growth is disrupted. Hair strands naturally grow, shed, and regenerate in phases called anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting/shedding). Most people lose 50 to 100 hairs daily as part of this normal process. However, when new hair doesn’t replace lost hair, or when excessive shedding occurs, hair thinning or baldness can result.
Many factors influence hair loss, from genetics and hormonal changes to lifestyle habits and medical conditions. While some hair loss is temporary, others may be permanent and require medical intervention.
Types of Hair Loss
There are several types of hair loss, each with unique causes, symptoms, and treatments. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)
What it is: Androgenetic alopecia is hereditary and is the most common form of hair loss. It affects both men and women. Hair follicles shrink over time due to sensitivity to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), resulting in thinner and shorter hair.
Symptoms:
- Men typically experience a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, forming an “M” shape.
- Women notice overall thinning, with a widening part at the scalp.
Treatment Options:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical solution that stimulates hair growth.
- Finasteride (Propecia): An oral medication that blocks DHT (for men only).
- Hair transplants and PRP therapy can help in advanced cases.
2. Alopecia Areata
What it is: An autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss in smooth, round patches.
Symptoms:
- Sudden development of bald patches on the scalp or body.
- The affected areas are typically smooth and may feel itchy before hair falls out.
Treatment Options:
- Steroid injections: Reduce inflammation and encourage hair regrowth.
- Topical immunotherapy: Triggers a controlled skin reaction to re-stimulate hair follicles.
3. Telogen Effluvium
What it is: A temporary condition caused by a disruption in the hair growth cycle, leading to diffuse thinning of hair across the entire scalp.
Causes:
- Significant stress (e.g., job loss, bereavement).
- Hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, menopause).
- Nutritional deficiencies (e.g., iron).
- Illness or medications.
Symptoms: Increased hair shedding, especially when brushing or washing, typically 2–3 months after the triggering event.
Treatment Options:
- Addressing the underlying cause (e.g., managing stress or correcting deficiencies).
- Hair tends to regrow on its own within six months to a year.
4. Traction Alopecia
What it is: Hair loss caused by constant tension or pulling on the hair follicles. This often results from wearing tight hairstyles like ponytails, braids, or extensions.
Symptoms:
- Thinning around the hairline or temples.
- Redness or sore spots on the scalp.
Treatment Options:
- Avoid tight hairstyles and take breaks from styling.
- If caught early, hair can regrow naturally. Severe cases may require minoxidil or hair transplants.
—-
5. Anagen Effluvium
What it is: Rapid hair loss caused by medical treatments such as chemotherapy, which affects the hair’s growth phase (anagen).
Symptoms: Sudden thinning or complete loss of hair, often within days to weeks of starting treatment.
Treatment Options:
- Hair typically regrows after the treatment is completed.
- Temporary solutions like wigs or scarves can help during recovery.
6. Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia)
What it is: A rare, irreversible condition where inflammation destroys hair follicles and replaces them with scar tissue.
Causes: Autoimmune disorders, infections, or severe skin conditions may damage hair follicles.
Symptoms:
- Gradual patchy hair loss accompanied by redness, itching, or swelling of the scalp.
- Shiny, scarred areas where hair follicles once existed.
Treatment Options:
- Anti-inflammatory treatments like corticosteroids may help if caught early.
- Hair transplantation is an option in specific cases.
7. Trichotillomania (Hair-Pulling Disorder)
What it is: A psychological condition where individuals feel a compulsive urge to pull out their hair, often triggered by stress, anxiety, or boredom.
Symptoms:
- Noticeable hair thinning or bald spots where pulling occurs.
- The person may feel relief after pulling their hair.
Treatment Options:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps manage compulsive behaviors.
- Medications for underlying anxiety or OCD may also help.
8. Hormonally-Induced Hair Loss
What it is: Hormonal imbalances during pregnancy, menopause, or due to thyroid disorders can lead to hair thinning.
Symptoms: Hair thinning around the scalp or crown, often with increased shedding.
Treatment Options:
- Treat underlying hormonal conditions (e.g., thyroid medications or hormone therapy).
- Proper nutrition and supplements like biotin can support hair health.
Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of hair loss early can help you take timely action. Look out for the following symptoms:
- Thinning hair around the hairline, temples, or scalp crown.
- Excess hair in your brush, pillow, or shower drain.
- Bald patches on the scalp or other parts of the body.
- Irritated or inflamed scalp.
Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss can result from multiple factors, including:
- Genetics: The leading cause for androgenetic alopecia.
- Stress and Trauma: Major triggers for telogen effluvium.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of iron, zinc, or biotin.
- Medications: Chemotherapy, blood thinners, or hormonal treatments.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like alopecia areata attack hair follicles.
Take Action on Hair Loss
If you’re experiencing symptoms of hair loss, consulting a dermatologist is key. They may perform diagnostic tests, such as scalp biopsies, blood tests, and hair analysis, to identify the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatments.
Treatments for Hair Loss
Depending on the type of hair loss, these treatments can help:
- Medications: Minoxidil and finasteride for pattern baldness.
- Corticosteroids: Effective for inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
- PRP Therapy: Promotes hair regrowth using your blood plasma.
- Hair Transplants: Permanent solution for certain types of alopecia.
- Lifestyle Changes: Stress reduction, proper hair care, and a balanced diet.
Tips to Prevent Hair Loss
While not all forms of hair loss are preventable, maintaining a healthy scalp and hair is a good start:
- Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on hair strands.
- Use gentle shampoos and conditioners free of harsh chemicals.
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet with adequate iron, biotin, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Manage stress through exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques.
Seek Expert Help for Hair Loss
Dealing with hair loss can feel overwhelming, but with early diagnosis and proper treatment, many cases can be managed effectively. Consult a dermatologist to explore personalized solutions tailored to your condition. Remember, the sooner you act, the better the outcome!







